The SELinux (Security Enhanced Linux) is a feature of Linux operating systems which bullet poofs your system against security holes even if you accidentally chmod a file or directory to 777. It uses file contexts to find which files belongs to what type. SELinux operates in many different modes and this article I’ll show you how to switch between these modes temporarily or permanently. I’ll also show you how to disable selinux completely, but be warned do not do this unless you know what you’re doing.Continue Reading…
Change Linux Login banner
Banner screens provide a lot of important and warm welcome messages, but they also expose the system to a number of threats by displaying the exact version number. In Linux by default after your system starts when you come to the terminal you may see a screen like this
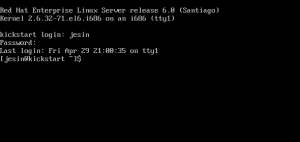
You can customize this banner according to your liking to add a personalized message or to make it more informative.Continue Reading…
Linux iptables LOG everything
Using iptable’s LOG action certain things in the network tracffic can be logged. In this article I’ll explain how to log each and every minute network traffic using iptables. You can choose which Chain rules and tables should be logged. Information on network traffic is stored in /var/log/messages. This information can be very useful for debugging firewall rules or when you are configuring NAT. Continue Reading…
Continue Reading…
RHCE exam experience
In this article I’ll be sharing my experience of going through RHCE exam and a few tips on how to crack the one-of -the-kind performance based exams. Before I proceed let me tell you that I will NOT be sharing any exam questions because I’ve agreed to the NDA (Non Disclosure Agreement). For those who haven’t heard RHCE (Red Hat Certified Engineer) is a certification offered by Red Hat Inc. for which you have to pass two “performance” based exams, RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) and RHCE. Performance based means you have to practically configure everything on the system they provide no objective type questions or theoretical ones where you can practice a couple of “dumps” and breeze through it.Continue Reading…
How to unregister RHN (Red Hat Network)
The RHN (Red Hat Network) is a service provided by Red Hat for receiving updates and support for your Red Hat Enterprise Linux installation. A RHEL copy can be added to RHN by executing the rhn_register command. If for some reason you want to unregister a machine from your RHN network login to RHN from http://rhn.redhat.com/ select you system and click “Delete System” located on the top right.
It isn’t over yet because your computer still “thinks” it is a part of RHN network. To unregister the computer a file has to be removed. Login as root user and execute the following command
rm /etc/sysconfig/rhn/systemid
if you aren’t comfortable with the command line open a file browser with super user permissions (root) navigate to /etc/sysconfig/rhn and delete the file systemid. You can execute rhn_register to reregister that system in future.
SSH verify host public key
Usually when you connect to a computer via SSH for the first time you might see a message stating “The authenticity of the host can’t be established Are you sure you want to continue connecting ?” even if you blindly give yes it has a lot of meaning in it. If you’re accessing your workplace computer through SSH just by entering ssh server.workplace.com you can’t be sure the connection is between you and your workplace server. A malicious user tampering with your internet connection can also create a man-in-the-middle attack and find out your Linux user account password. By importing the public key of the host to which you’re connecting you can be sure you’re “talking” to the right person.Continue Reading…
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- Next Page »



